American Ergonomics Corporation
Innovative Seat Technology for Comfort and Safety
How It Works
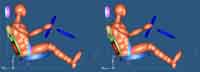
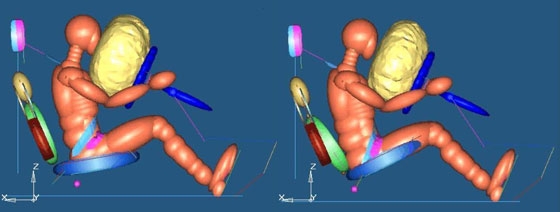
The arcuate path of motion of the CBM Seat acts as a safety restraint. The easiest explanation of crash dynamics with the CBM Seat is illustrated above. In a typical frontal impact, the occupant continues forward and is restrained by the belt and airbag, with virtually no safety contribution from the seat. In this illustration, the traditional seat is compared to the CBM Seat at 50 milliseconds into a crash simulation.
The traditional seat shows visible space between the lower backrest and the driver's back. The body is sliding forward and escaping the seat. With the CBM Seat, the driver's lower back is still in contact with the lumbar support and, more importantly, the face is not yet in contact with the airbag.
The angles of the seat pan from the horizontal plane are notably different. With the CBM Seat, effective deceleration has already begun. The CBM Seat acts as the third occupant restraint. Even before the seat belt or airbag can act, the CBM Seat begins to dissipate upper and lower body impact forces instantaneously.
The traditional seat shows visible space between the lower backrest and the driver's back. The body is sliding forward and escaping the seat. With the CBM Seat, the driver's lower back is still in contact with the lumbar support and, more importantly, the face is not yet in contact with the airbag.
The angles of the seat pan from the horizontal plane are notably different. With the CBM Seat, effective deceleration has already begun. The CBM Seat acts as the third occupant restraint. Even before the seat belt or airbag can act, the CBM Seat begins to dissipate upper and lower body impact forces instantaneously.